GAN(생성적 대립 신경망)
- GAN의 원리는 간단하다.
- 유명한 골키퍼 앞에서 패널티킥 연습을 엄청 해서 골을 넣기 시작했다면, 피널티킥 슛팅하는 기술이 금새 늘어나는 원리이다.
- 생성모델(슈터)과 판별모델(골키퍼) 두 모델이 대립적인 과정을 통해 동시에 훈련된다.
- 위조지폐를 만들려는 ‘위조지폐범’이 지폐를 위조하지 못하게 하고, 또 위조지폐와 진폐를 잘 가려내고 싶은 ‘조폐공사’가 있다.
- 조폐공사는 위폐를 감별하는 기술을 지폐에 적용해야 한다.
- 반대로 위조지폐범은 감별하는 기술에 걸리지 않는 위조지폐를 만들려고 기술을 발전 시킨다.
- 서로의 정보를 참고해서 기술이 발달되기 때문에 지폐를 제작하는 기술이 점점 좋아지게 된다.
- 이를 ‘인공지능 화가’에 적용하면, Creator/Generator는 진짜 작품처럼 보이는 이미지를 생성하도록 배우게 되고, 동시에 Descriminator는 인공지능이 만든 가짜의 이미지와 진짜를 예술작품을 구별하게 되는 것을 배우게 되는 원리이다.
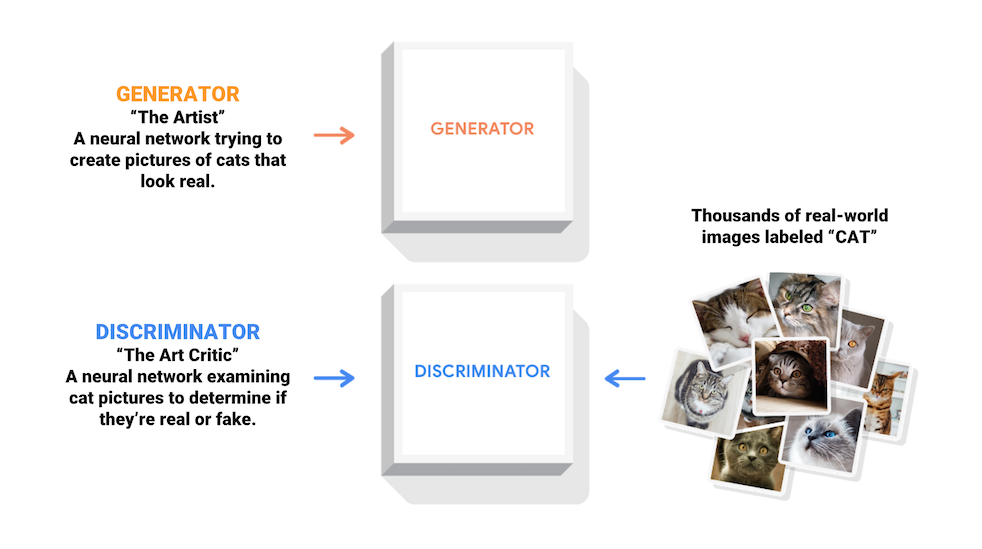
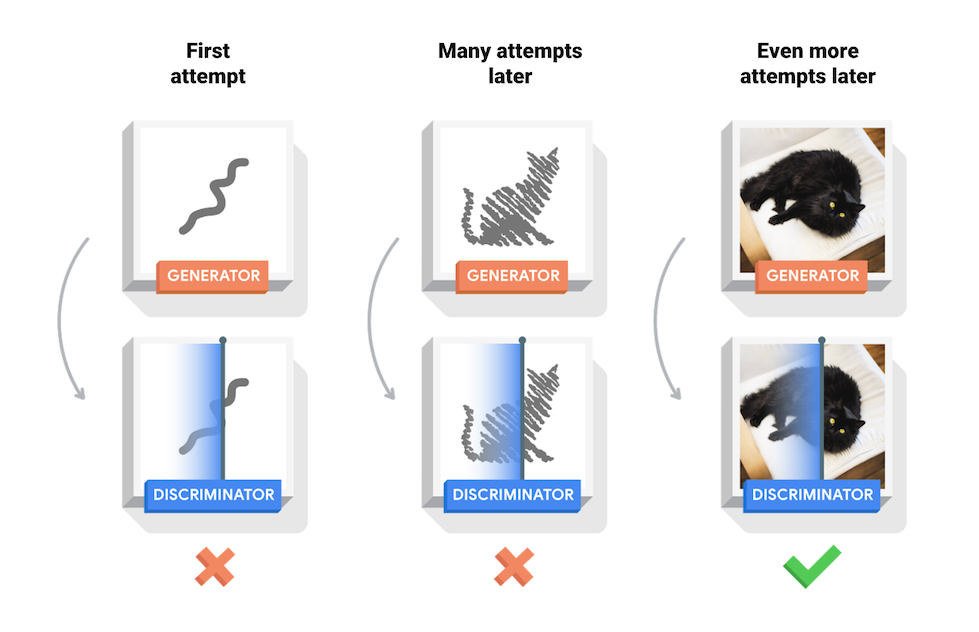
- 훈련과정동안 Generator는 점차 실제같은 이미지를 더 잘 생성하게 되고, Descriminator는 점차 진짜와 가짜를 더 잘 구별하게 된다.
- 이 과정은 Descriminator가 가짜 이미지에서 진짜 이미지를 더 이상 구별하지 못하게 될 때, 평형상태에 도달하게 된다.
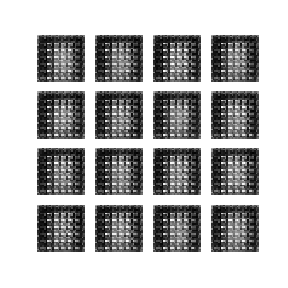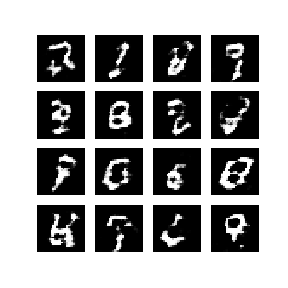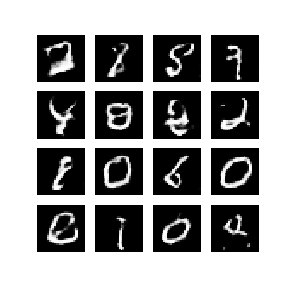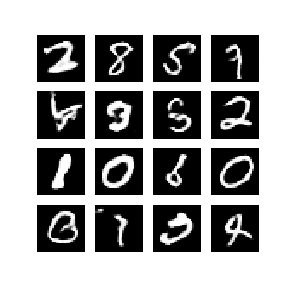
- 위 이미지는 50epoch동안 훈련한 Generator가 생성해낸 연속된 이미지이다.
- 이미지들은 랜덤한 잡음으로부터 시작되어, 점차 시간이 지남에 따라 손으로 쓴 숫자를 닮아가게 된다.
- MIT의 Intro to Deep Learning 수업

- 위 그림은 네트워크 구조이다.
- autuencoder를 중심부터 바깥쪽으로 뒤집어 둔 개념이다.
1 | |
DCGAN
Generator(생성자)
- 생성자는 시드값(seed; 랜덤한 잡음)으로부터 이미지를 생성하기 위해
Conv2D(업샘플링) 층을 이용한다. - 처음 Dense 층은 이 시드값을 인풋으로 받는다.
- 그 다음 원하는 사이즈의 28 * 28 * 1의 이미지가 나오도록 업샘플링을 여러번 한다.
- tanh를 사용하는 마지막 층을 제외한 나머지 각 층마다 활성 함수로
LeakyReLU를 사용한다.
1 | |

Discriminator(감별자)
- 감별자는 합성곱 신경망(CNN) 기반의 이미지 분류기이다.
1 | |
손실함수와 옵티마이저 정의
1 | |
감별자 손실함수
- 감별자가 가짜 이미지에서 얼마나 진짜 이미지를 잘 판별하는지 수치화한다.
- 진짜 이미지에 대한 감별자의 예측과 1로 이루어진 행렬을 비교하고, 가짜 이미지에 대한 감별자의 예측과 0으로 이루어진 행렬을 비교한다.
1 | |
생성자 손실함수
- 생성자의 손실함수는 감별자를 얼마나 잘 속였는지에 대해 수치화한다.
- 직관적으로 생성자가 원활히 수행되고 있다면, 감별자는 가짜 이미지를 진짜로 분류할 것이다.
- 생성된 이미지에 대한 감별자의 결정을 1로 이루어진 행렬과 비교할 것이다.
1 | |
체크포인트 저장
- 오랜 시간 진행되는 훈련이 방해되는 경우 유용하게 쓰일 수 있도록 학습 중간에 모델의 저장방법과 복구방법을 보여준다.
1 | |
훈련 루프 정의
- 훈련 루프는 생성자가 입력으로 랜덤 시드를 받는 것으로부터 시작된다.
- 그 시드값을 사용하여 이미지를 생성한다.
- 감별자를 사용하여 (훈련 세트에서 갖고 온)진짜 이미지와 (생성자가 생성해낸)가짜 이미지를 분류한다.
- 각 모델의 손실을 계산하고, gradients를 사용해 생성자와 감별자를 업데이트한다.
1 | |
모델 훈련
train()메소드를 생성자와 감별자를 동시에 훈련하기 위해 호출한다.- 생성적 대립 신경망을 학습하는 것은 까다로울 수 있다.
- 생성자와 감별자가 서로 제압하지 않는 것이 중요하다.(학습률이 비슷하면 한쪽이 우세해진다.)
- 훈련 초반부에 생성된 이미지는 랜덤한 노이즈처럼 보인다.
- 훈련이 진행될수록, 생성된 숫자는 점차 진짜처럼 보일 것이다.
- 약 50epoch가 지난 후, MNIST 숫자와 닮은 이미지가 생성된다.
1 | |

1 | |
GIF 생성
1 | |

1 | |
CycleGAN
- 위에서 배운 DCGAN의 구조를 변경해서 새로운 아키텍쳐를 생성했다.
- 이번에는 쌍을 이루는 이미지를 볼 수 있는데, 굳이 쌍이 없더라도 학습과 테스트를 해볼 수 있도록 만들어진 것이 해당 논문의 핵심이었다.
- 페어링되지 않은 이미지 대 이미지 변환을 보여준다.
- 이 논문은 한 이미지 도메인의 특성(얼룩줄무늬)을 캡쳐하고 이러한 특성을 다른 이미지 도메인(말;)으로 변환할 수 있는 방법을 알아낼 수 있는 방법을 제안한다.
- CycleGAN이라고도 알려진 Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks를 사용한 예시를 볼 수 있다.
- 그림 vs 사진
- 얼룩말 vs 말
- 여름 vs 겨울
- 화가 변환
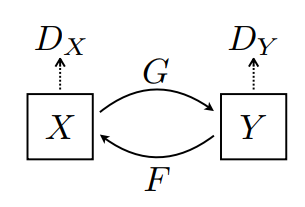
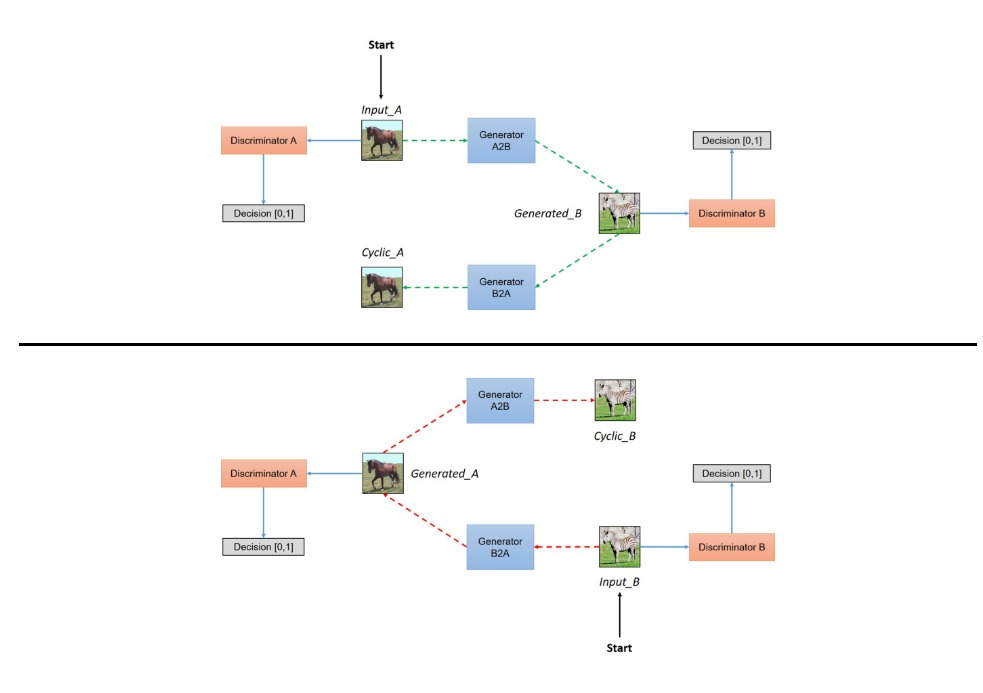
- CycleGAN은 주기 일관성 손실을 사용하여 쌍을 이루는 데이터 없이도 훈련을 가능케 한다.
- 소스 및 대상 도메인 간의 일대일 매핑 없이 한 도메인에서 다른 도메인으로 변환할 수 있다.
- 해상도 향상, 사진의 그림화, 스타일 변환 등과 같은 많은 흥미로운 작업을 수행할 수 있는 가능성을 열어준다.
-
필요한 것은 소스와 대상 데이터셋뿐이다.
- 과일의 종류를 바꾸는 예시

- 사진 속 계절을 변경하는 예시

실습
1 | |
Input Pipeline
- 말 이미지에서 얼룩말 이미지로 변환하는 모델을 학습시킨다.
- 훈련 데이터셋에 무작위 지터링하고, 미러링하여 학습에 이용되도록 설계되어 있다.
- 과적합을 방지하는 이미지 확대 기술 중 일부이다.
- 무작위 지터링에서 이미지는 286 * 286 크기가 조정된 다음 무작위로 256 * 256으로 잘린다.
- 랜덤 미러링에서는 이미지가 좌우로 무작위로 뒤집힌다.
1 | |

1 | |

1 | |

Review
- 다른 종류의 GAN
- Least Squares GAN : LSGAN
- Semi-Supervised GAN : SSGAN, Class 분류와 동시에 진위여부를 확인하는 GAN
- Auxiliary Classifier GAN : Class, noise를 이용하여 만들어내는 GAN
- Stack GAN : Text를 이용해서 이미지를 생성하는 GAN
- Cycle GAN : 그림을 사진으로, 사진을 그림으로, 말을 얼룩말로 얼룩말을 말로!!
- Disco GAN : Cycle GAN과 유사, 가방에 신발 디자인을 반영하는 Cross Modality GAN
- Design GAN : 새로운 디자인 티셔츠를 만들기
- Style GAN : 1024x1024 고화질의 이미지를 만들어내는 GAN
- Adapitve instance normalizaton : AdaIN - Style transfer
